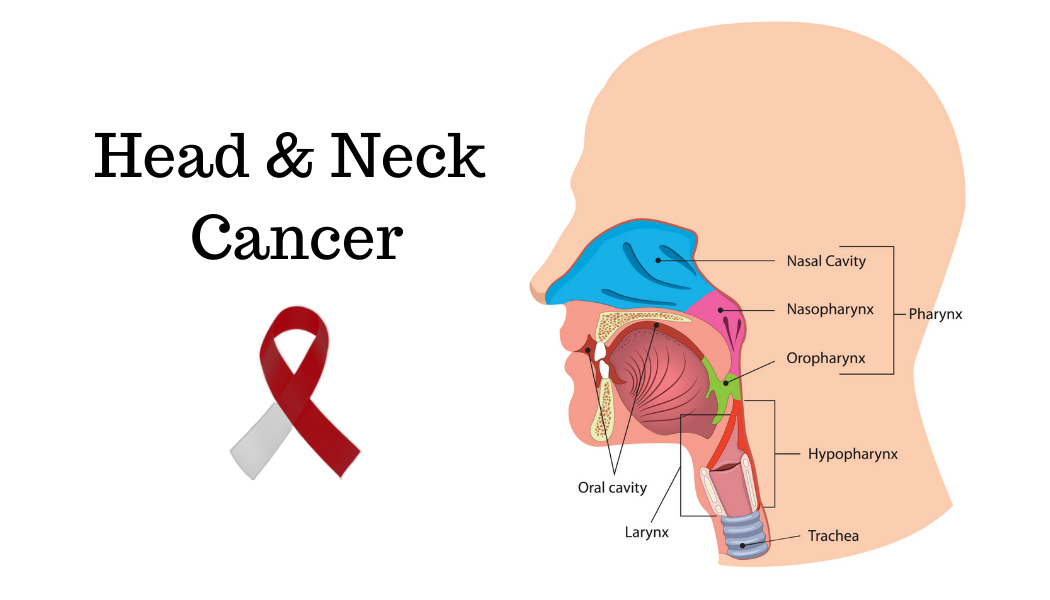
Head And Neck Cancer
- Persistent sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Changes in voice or hoarseness
- Lump or swelling in the neck
- Pain or difficulty chewing or moving the jaw
- Ear pain or hearing loss
Diagnosis:

Health Tips & Info
about head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that develop in the head and neck region. This includes cancers affecting the mouth, tongue, throat, voice box (larynx), salivary glands, sinuses, and nasal cavity. Head and neck cancers typically arise from the squamous cells lining the moist surfaces inside the head and neck, such as the mucous membranes.
symptoms
The signs and symptoms of head and neck cancer vary depending on the specific site of the tumor but may include:
- A persistent sore throat.
- Pain or difficulty chewing or moving the jaw
- Lump or swelling in the neck
- Changes in voice or hoarseness,/li>
- Trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Ear pain or hearing loss
- Numbness or weakness in the face
- Persistent nasal congestion or nosebleeds
Diagnostic Test
Here are some common diagnostic tests used for head and neck cancer:
1.Physical Examination: The doctor will perform a thorough examination of the head and neck region, looking for any abnormal lumps, swelling, or changes in the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat. They may also assess the function of the vocal cords and examine the lymph nodes in the neck.
2. Imaging Tests: Imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the inside of the body and help identify the location and size of tumors. Common imaging tests for head and neck cancer include:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the head and neck region.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce detailed images of the soft tissues. It provides more detailed information about tumors and their relationship to surrounding structures.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: A PET scan uses a radioactive tracer to detect areas of high metabolic activity, which can indicate cancerous cells.
4.Biopsy: A biopsy is the definitive diagnostic test for head and neck cancer. It involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the suspected tumor or abnormal area. The sample is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine if cancer cells are present.
5. Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): If there is a suspicious lump or enlarged lymph node in the neck, a fine needle aspiration may be performed. A thin needle is inserted into the lump to extract cells for examination. This helps determine if the lymph node contains cancer cells.
Conditions and Treatments
conditions and treatments associated with head and neck cancer:
1. Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of head and neck cancer, and it arises from the squamous cells lining the oral cavity, throat, voice box, and other areas of the head and neck. Treatment options for squamous cell carcinoma include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
2. Oral Cavity Cancer: Oral cavity cancer refers to cancer that develops in the lips, tongue, gums, and lining of the mouth. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the tumor, and it may be combined with radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
3. Oropharyngeal Cancer: Oropharyngeal cancer affects the back of the throat, including the base of the tongue and tonsils. Treatment may involve a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may also be used.
4. Laryngeal Cancer: Laryngeal cancer affects the voice box (larynx) and can cause changes in voice or hoarseness. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Depending on the extent of the cancer, partial or total removal of the larynx (laryngectomy) may be necessary.
5. Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer: Cancer that develops in the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses may require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In some cases, specialized surgical procedures, such as endoscopic surgery, may be used to remove the tumor.
6. Salivary Gland Cancer: Salivary gland cancer can occur in the salivary glands located in the mouth, neck, and throat. Treatment options include surgery to remove the affected gland, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, chemotherapy.
7. Reconstructive Surgery: Depending on the extent of the cancer and the surgical treatment required, reconstructive surgery may be performed to restore the appearance and function of the head and neck region. This may involve techniques such as skin grafts, tissue flaps, or prosthetic devices.
8. Rehabilitation and Supportive Care: Head and neck cancer and its treatments can affect various functions such as swallowing, speaking, and breathing. Rehabilitation and supportive care play a crucial role in helping patients regain these functions and improve their quality of life. This may involve speech therapy, swallowing exercises, dental or prosthetic interventions, nutritional support, and psychological counseling.
Treatment Available
There are several treatment options available for head and neck cancer. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the location, stage, and extent of the cancer, as well as the overall health of the patient. Here are some common treatment modalities for head and neck cancer:
1. Surgery: Surgery is often used to remove the cancerous tumor and nearby tissues. The extent of surgery depends on the location and stage of the cancer. Surgical procedures may include:
- Transoral Surgery: Minimally invasive procedures performed through the mouth, such as transoral robotic surgery (TORS) or transoral laser microsurgery (TLM), can be used to remove tumors in the oral cavity, throat, or larynx.
- Neck Dissection: In cases where cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, a neck dissection may be performed to remove the affected lymph nodes.
- Laryngectomy: In advanced laryngeal cancer, a partial or total removal of the larynx (voice box) may be necessary to eliminate the cancer.
- Reconstructive Surgery: After tumor removal, reconstructive surgery may be performed to restore the appearance and function of the head and neck area.
3. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is often used in combination with radiation therapy (chemoradiation) to enhance treatment effectiveness. Chemotherapy may also be used as a primary treatment for advanced or metastatic head and neck cancer.
4. Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs specifically target certain abnormalities in cancer cells to inhibit their growth and division. These drugs may be used in combination with other treatments or as a standalone treatment for head and neck cancer.
5. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy aims to enhance the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab, have shown promise in treating certain types of head and neck cancers, particularly those associated with human papillomavirus (HPV).
6. Palliative Care: Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms, improving quality of life, and providing support for patients with advanced or incurable head and neck cancer. Palliative treatments may include pain management, symptom control, and psychological support.
cost
|
type of treatment
|
USD
|
BDT
|
INR
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Oral Cavity Cancer
|
$10,000 to $100,000
|
-
|
INR 1,50,000 to INR 6,00,000
|
|
Oropharyngeal Cancer
|
$20,000 to $100,000
|
-
|
INR 2,00,000 to INR 10,00,000
|
|
Laryngeal Cancer
|
$20,000 to $100,000
|
-
|
INR 2,00,000 to INR 10,00,000
|









